
In water, the speed of sound is 1480 m/s. Alternatively, sound moves quicker in water than in air. Speed of Sound in Water: The speed of sound in water exceeds that of air.This is obviously not the case for solids and liquids. Since gases expand to fill a given vacuum, their density is very uniform regardless of the type of gas. Speed of Sound in Gas: When sound approaches a liquid or solid, the speed of sound is independent of the density of the medium.As a result, the speed of sound in liquids is intermediate between the speeds of sound in solids and gases. As a result, the distances between molecules in liquids are greater than in solids but smaller than in gases. Speed of Sound in Liquid: A liquid’s density is higher than a gas’s density.Another fascinating finding about sound speed is that sound moves 35 times faster in diamonds than in air. The speed of sound in solid is 6000 m/s, while the speed of sound in steel is 5100 m/s. Because of this advantage, the speed of sound in a solid is greater than that of a gas. It takes less time for a stable molecule to collide with its neighboring molecule. Because of their near proximity due to mass, they will collide very easily. This suggests that in solids, molecules are closer to each other than in liquids, and in liquids, molecules are closer to each other than in gases. Solids are much denser than liquids or gases. Speed of Sound in Solid: Sound is nothing more than a vibration caused by particle collisions one molecule colliding with the next, and so on.Speed of Sound in Different Media at 25 ✬ However, none of the gases we encounter in everyday life are ideal gases, and as a result, their properties vary slightly. In gases, the speed of sound is equal to the square root of the absolute temperature (measured in Kelvin), but it is unaffected by the frequency of the sound wave, strain, or density of the medium. In general, sound waves fly the fastest through solids, then liquids, and finally gases. The table below shows the speed of sound in various media. The medium is the matter in which the waves pass. Sound waves are mechanical waves that can only pass through matter. In any medium, as we increase the temperature, the speed of sound increases. The speed of sound decreases when we go from a solid to a gaseous state. The speed of sound depends on the properties of the medium through which it travels. Sound travels 4 times faster in water (1,482 meters per second) and around 13 times faster through steel (4,512 meters per second). At this rate sound will travel one mile in around five seconds. The distance traveled per unit time by a sound wave propagating through a medium is referred to as the speed of sound.Īt 20 ☌, the speed of sound in air is 343.2 m/s, which corresponds to 1,236 km/h. The speed of sound is an important parameter in many fields of physics. As a result, as the temperature rises, so does the speed of sound. Temperature of the medium: The temperature of the medium and the frequency of the sound waves are strictly proportional.As a result, as the density of the medium increases, so does the speed of sound. When the medium is thick, the molecules in the medium are tightly packed, causing sound to propagate further. Density of the medium: There is a need of medium for sound waves to travel, and the density of the medium is assumed to be one of the influences on which the speed of sound depends.ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.

GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.
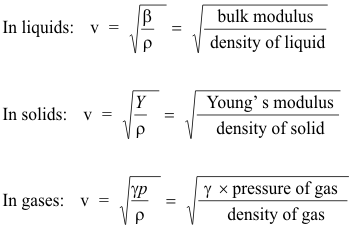
Newton’s formula for the speed of sound, $v=\sqrt$ lies in the specified range of $(0.350\pm 0.005)$ m. Note that adiabatic bulk modulus of an ideal gas at pressure $p$ is $B=\gamma p$ and its density is $\rho=pM/RT$. Where $\gamma$ is the adiabatic index (ratio of specific heats), $R=8.314$ J/mol-K is the universal gas constant, $T$ is the absolute temperature and $M$ is the molecular mass.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
